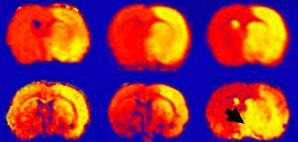
We develop novel neuroimaging tools to better quantify brain edema and blood-brain barrier integrity in the setting of cerebral ischemia. By creating high specificity methods using non-invasive imaging, we have advanced our understanding of the role brain edema plays in modulating neurological recovery after stroke. These studies have revealed that brain edema may impact recovery in up to 25% of all stroke patients. Our imaging tools not only provide insight into the pathophysiology of secondary brain injury, but can also serve as intermediate endpoints in clinical trials as part of proof of concept studies for anti-edema treatments.
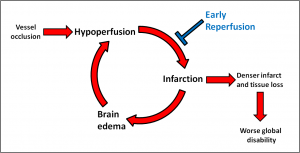
We hypothesize that brain edema is associated with a cycle of neuronal injury. The initial ischemic insult occurs with blood vessel occlusion. The resulting hypoperfusion leads to tissue infarction. Brain edema, which ensues 12 to 48 hours after the initial ischemic injury, exacerbates hypoperfusion, which in turn amplifies neuronal loss within the existing stroke lesion. We believe this cascading cycle of hypoperfusion and infarction leads to greater brain injury and ultimately, worse neurological function. Using stroke cohorts with serial brain imaging, our studies seek to build evidence for each segment of this cycle.
Portable, low-field (LF) MRI could provide significant value in the early evaluation of stroke. LF-MRI has also been investigated by the Kimberly Lab in other domains, including Alzheimer’s disease and HIV. Ongoing work seeks to explore the use of this technology in new domains, and augment its use with machine learning.